If your payroll captures labor cost by employee, project, and task, then you may be able to post actual labor cost against your projects and would not need Sage Intacct Labor Costing.
Understanding Labor Costing
For many customers, Payroll is posted at a summary level. This is where labor costing through the Timesheet module comes in. Labor costing will multiply Hours Worked on Each Project/Task by a Cost Rate. These Project Labor costs will post to the general ledger which gets sent to accounts outside of your regular financial accounts (such as 9xxx) and should be put into the Manpower Cost category, which will exclude them from all standard financial reports. These are estimated labor costs used for project costing; your actual labor cost will come from Payroll. The 9xxx accounts will be used in Project Financial reports to show estimated labor costs per Project; they should be excluded from standard financial reports.
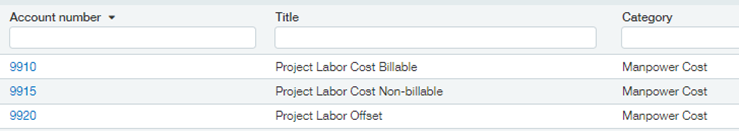
Options for Labor Cost Rate
On the Employee record, indicate Hourly or Salary and enter the hourly rate or annual salary on the Cost rates tab. Be sure to enter a Start date that will be used as the effective date. The three options for labor cost rate are:
- Hourly Rate: This could be an actual cost or a loaded cost. This can also be used for salaried employees instead of the salary options. This rate will be multiplied by hours worked and posted as labor cost against each project.
- Salary with Variance
- Salary without Variance
Salaried Labor Costing
When an employee is marked salary, the annual salary is entered, but Intacct will calculate an hourly rate for costing. If an employee works 40 hours, then the hourly cost is calculated as: Salary/2080 hours.
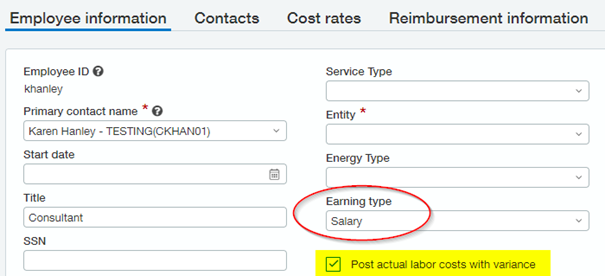
Understanding the Implications of the "Post Actual Labor Costs with Variance" Flag
Example: Employee has an annual salary $41,600/Year or $800/week assuming a 40 hour week. Intacct will calculate an hourly wage for costing this Employee to a Project. In examples below, this employee worked 50 hours on three different projects.
- 40 hour cost allocation = $800 ($20/hour)
- 50 hour cost allocation at $20/hour = $1000
- Variance = 200
- Prorated cost allocation = $800 / 50 hours ($16/hour)
When we allocate salaried employee to projects, do we want to allocate $20/hour or $16/hour?
- If you select $20/hour, then you wan to post to the variance account
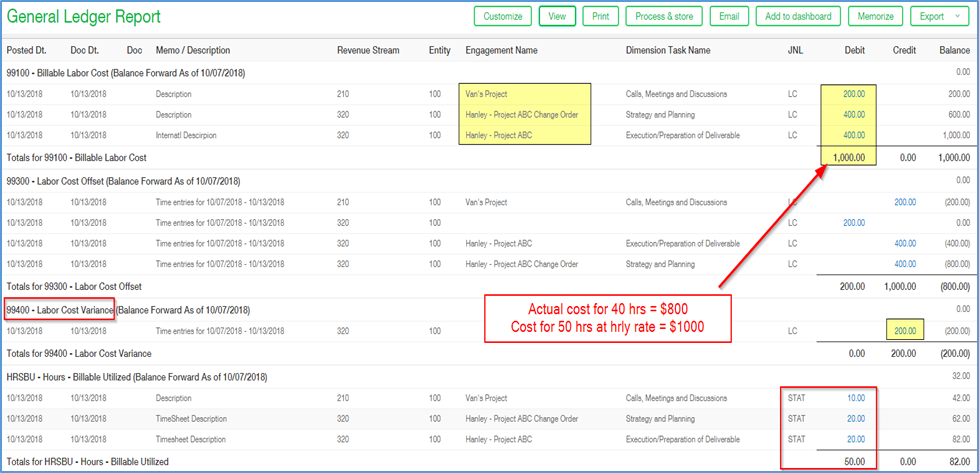
Example #1: Cost Variance
You have a salary employee with more than 40 hours who is working on multiple projects and the Flag is checked to Post with variance. Cost is calculated as actual hours worked (50) multiplied by the standard hourly wage ($20).
- 50 hours * $20 = $1000
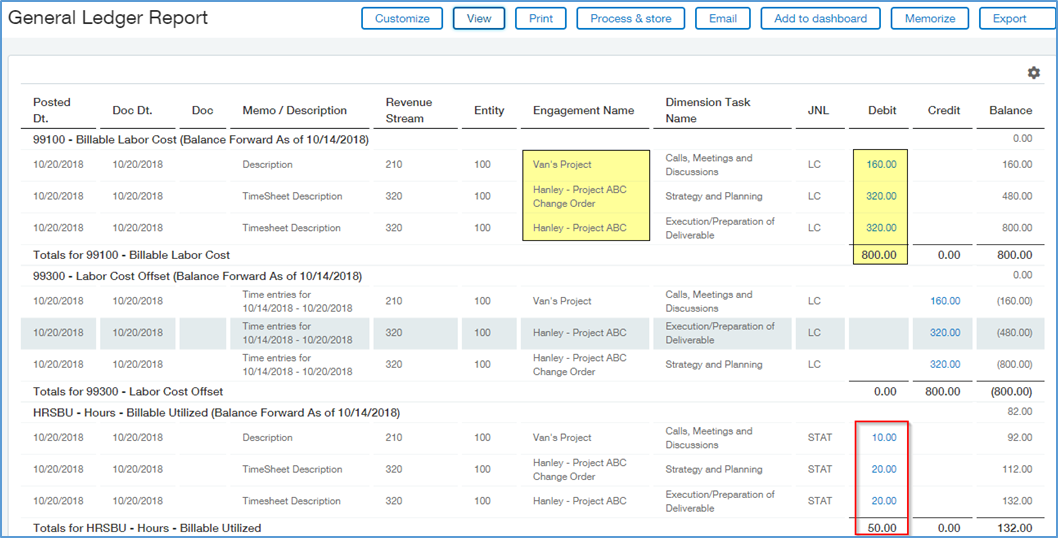
Example #2: DO NOT Check to Post to Variance
You have a salary employee with more than 40 hours who is working on multiple projects and the Flag is NOT checked. Cost is calculated as actual hours worked (50) multiplied by a prorated hourly wage ($16).
- 50 hours * $16 = $800
questions?
If you need assistance with Project Labor Costing and Salary Variance in Sage Intacct, please reach out to RKL Support.



